Table of Contents
Pyra = Fire
Mathias de Stefano
Mid = Middle
Built I the Great Pyramid, patterned after the pyramid of earth force, burning eternally so that it, too, might remain through the ages
The Emerald Tablets of Thoth
Dating the pyramid of Khufu
The Great Pyramid (Khufu) has been determined to be about 4600 years old by two principal approaches: indirectly, through its attribution to Khufu and his chronological age, based on archaeological and textual evidence; and directly, via radiocarbon dating of organic material found in the pyramid and included in its mortar.
The majority of recent chronological estimates date Khufu and his pyramid roughly between 2700 and 2500 BC.
Radiocarbon dating
Mortar was used generously in the Great Pyramid’s construction. In the mixing process ashes from fires were added to the mortar, organic material that could be extracted and radiocarbon dated. A total of 46 samples of the mortar were taken in 1984 and 1995, making sure they were clearly inherent to the original structure and could not have been incorporated at a later date. The results were calibrated to 2871–2604 BC.
The old wood problem is thought to be mainly responsible for the 100–300 year offset, since the age of the organic material was determined, not when it was last used. A reanalysis of the data gave a completion date for the pyramid between 2620 and 2484 BC, based on the younger samples.
In 1872 Waynman Dixon opened the lower pair of “Air-Shafts”, previously closed at both ends, by chiseling holes into the walls of the Queen’s Chamber. One of the objects found within was a cedar plank, which came into possession of James Grant, a friend of Dixon. After inheritance it was donated to the Museum of Aberdeen in 1946; however, it had broken into pieces and was filed incorrectly. Lost in the vast museum collection, it was only rediscovered in 2020, when it was radiocarbon dated to 3341–3094 BC.
It’s more likely that the Great Pyramid is from the Zep Tepi, or Atlantean Egypt, dating back as far as 15,000 BC. Based on Mathias de Stefano’s memories, the pyramid dates back to his time in Khem, around 10,000 BC.
Zep Tepi time – Energy plant
Egyptian time of the pharao’s
The Great Pyramid of Giza, the largest Egyptian pyramid, served as the tomb for pharaoh Khufu during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom. It was constructed in the early 26th century BC and took about 27 years to complete. As the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, it stands as the sole wonder that has largely remained intact over time. Situated at the northern end of the Giza pyramid complex, it is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site “Memphis and its Necropolis.”
Initially towering at 146.6 meters (481 feet) (481 feet (146.61 meters)), the Great Pyramid held the title of the world’s tallest human-made structure for over 3,800 years. However, due to the removal of its smooth white limestone casing, its current height is 138.5 meters (454 feet) (454.4 ft). The base measures approximately 230.3 meters (756 feet) (755.6 ft) square, with a total volume of around 2.6 million cubic meters (92 million cubic feet), including an internal hillock.
The dimensions of the pyramid were 280 royal cubits (146.7 m; 481.4 ft) high, a base length of 440 cubits (230.6 m; 756.4 ft), with a seked of 5+1/2 palms (a slope of 51°50’40”).
Constructed using 2.3 million large blocks, weighing a total of 6 million tonnes, the pyramid features stones of varying sizes and shapes. The outer layers were held together by mortar, with local limestone from the Giza Plateau serving as the primary construction material. Additional stones were brought by boat on the Nile, including white limestone from Tura for the casing and granite blocks weighing up to 80 tonnes from Aswan for the “King’s Chamber” structure.
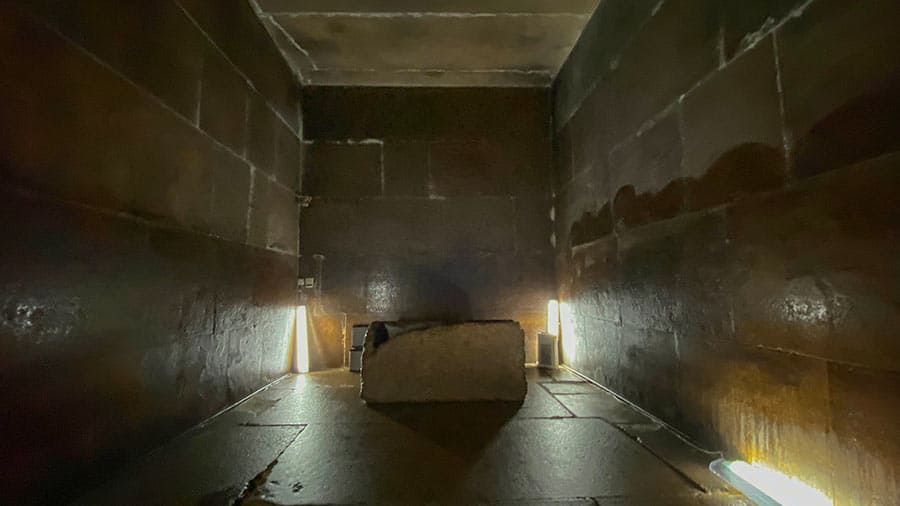
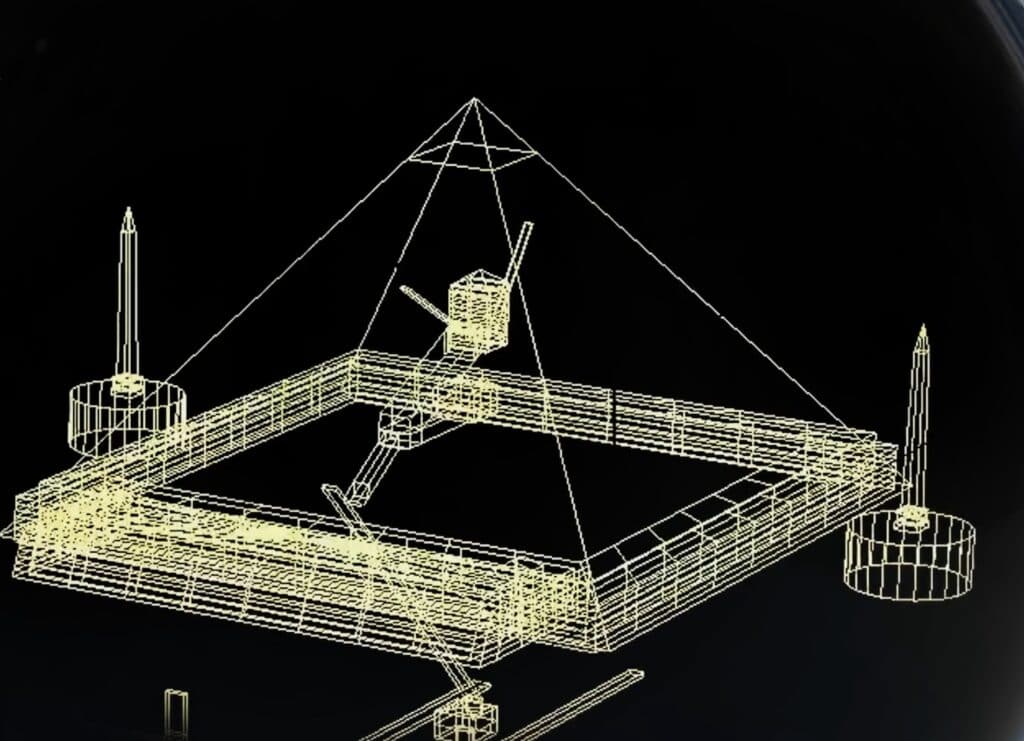
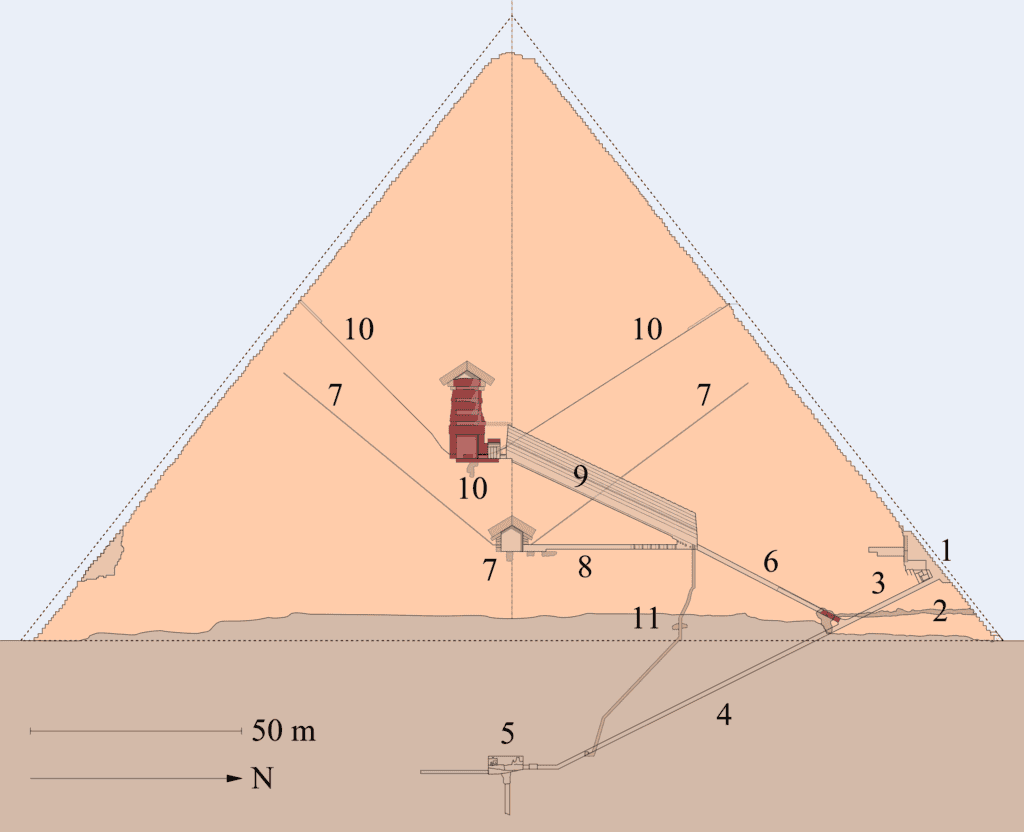
Inside the Great Pyramid, there are three known chambers. The lowest chamber was carved into the bedrock upon which the pyramid was built but was left unfinished. Above ground, within the pyramid structure, are the Queen’s Chamber and the King’s Chamber, containing a granite sarcophagus. Hemiunu, Khufu’s vizier, is believed by some to be the architect of the Great Pyramid. Various scientific and alternative hypotheses have been proposed to explain the exact construction techniques used.
The pyramid was part of a funerary complex that included two mortuary temples connected by a causeway (one near the pyramid and one close to the Nile), tombs for Khufu’s immediate family and court, three smaller pyramids for Khufu’s wives, a smaller “satellite pyramid,” and five buried solar barges. Near the pyramid, artifacts from the Maadi culture, dating back to the Fourth Millennium BC, were discovered, indicating previous settlements in the area.
Emerald Tablet I: The History of Thoth the Atlantean
Built I the Great Pyramid, patterned after the pyramid of earth force, burning
eternally so that it, too, might remain through the ages. In it, I built my knowledge of “Magic-Science” so that it might be here when again I return from Amenti. Aye, while I sleep in the Halls of Amenti, my Soul roaming free will incarnate, dwell among men in this form or another. (Hermes, thrice-born.)
Time to construct the Pyramid
As to the question of how over two million blocks could have been cut within Khufu’s lifetime, stonemason Franck Burgos conducted an archaeological experiment based on an abandoned quarry of Khufu discovered in 2017. Within it, an almost completed block and the tools used for cutting it had been uncovered: hardened arsenic copper chisels, wooden mallets, ropes and stone tools. In the experiment replicas of these were used to cut a block weighing about 2.5 tonnes (the average block size used for the Great Pyramid). It took four workers 4 days (with each working 6 hours a day) to excavate it. The initially slow progress sped up six times when the stone was wetted with water. Based on the data, Burgos extrapolates that about 3,500 quarry-men could have produced the 250 blocks/day needed to complete the Great Pyramid in 27 years.[91]
A construction management study conducted in 1999, in association with Mark Lehner and other Egyptologists, had estimated that the total project required an average workforce of about 13,200 people and a peak workforce of roughly 40,000.[92]
Precision
The first precise measurements of the pyramid were made by Egyptologist Flinders Petrie in 1880–1882, published as The Pyramids and Temples of Gizeh. Many of the casing-stones and inner chamber blocks of the Great Pyramid fit together with high precision, with joints, on average, only 0.5 millimetres (0.020 in) wide. On the contrary, core blocks were only roughly shaped, with rubble inserted between larger gaps. Mortar was used to bind the outer layers together and fill gaps and joints.
The block height and weight tend to get progressively smaller towards the top. Petrie measured the lowest layer to be 148 centimeters (4.86 ft) high, whereas the layers towards the summit barely exceed 50 centimeters (1.6 ft).
The accuracy of the pyramid’s perimeter is such that the four sides of the base have an average error of only 58 millimeters (2.3 inches) in length and the finished base was squared to a mean corner error of only 12 seconds of arc.
The completed design dimensions are measured to have originally been 280 royal cubits (146.7 m; 481.4 ft) high by 440 cubits (230.6 m; 756.4 ft) long at each of the four sides of its base. Ancient Egyptians used seked – how much run for one cubit of rise – to describe slopes. For the Great Pyramid a seked of 5+1/2 palms was chosen, a ratio of 14 up to 11 in.
Some Egyptologists suggest this slope was chosen because the ratio of perimeter to height (1760/280 cubits) equals 2π to an accuracy of better than 0.05 percent (corresponding to the well-known approximation of π as 22/7).