Table of Contents
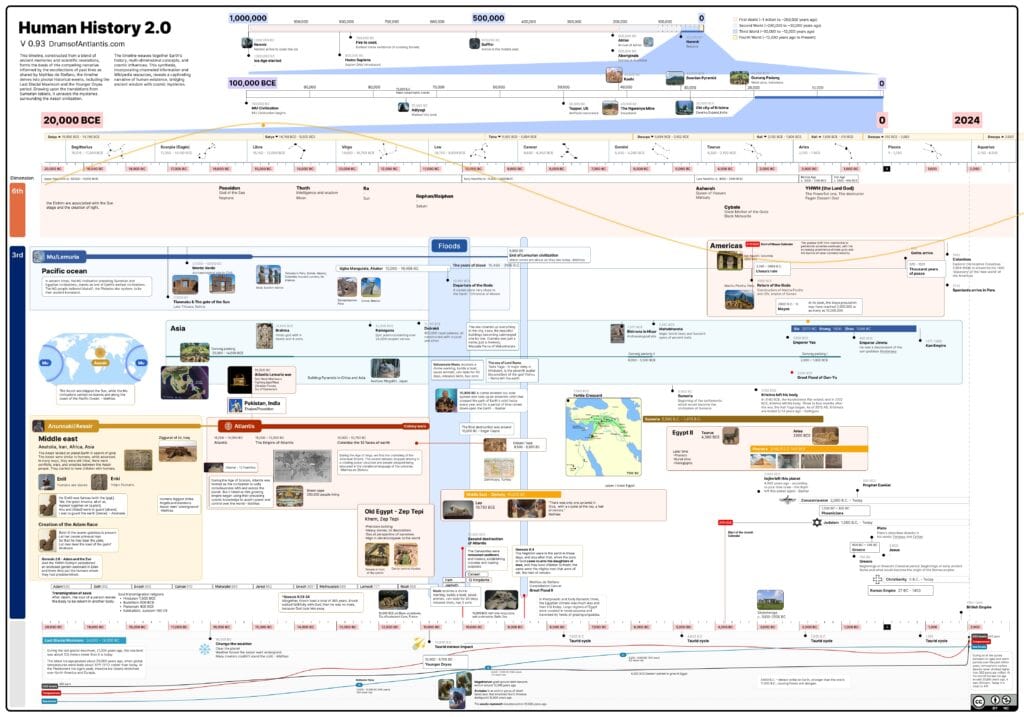
The structure of historical ages, such as the Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age, is primarily used by archaeologists, historians, and anthropologists to classify human prehistory and early history based on the dominant materials and technologies used at the time.
1. Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age)
- Time Period: circa 2.5 million BCE – 10,000 BCE
- Important Civilizations:
- Early human groups like Homo erectus and Homo sapiens
- Cave art cultures in Europe (Lascaux Cave, France) View
2. Mesolithic Age (Middle Stone Age)
- Time Period: circa 10,000 BCE – 8000 BCE
- Important Civilizations:
- Natufian culture in the Levant View
- Maglemosian culture in Northern Europe
3. Neolithic Age (New Stone Age)
- Time Period: circa 8000 BCE – 3000 BCE
- Important Civilizations:
4. Chalcolithic Age (Copper Age)
- Time Period: circa 4500 BCE – 3300 BCE
- Important Civilizations:
- Varna Culture in the Balkans (Bulgaria) View
- Uruk culture in Mesopotamia
5. Bronze Age
- Time Period: circa 3300 BCE – 1200 BCE
- Important Civilizations:
6. Iron Age
- Time Period: circa 1200 BCE – 539 BCE
- Important Civilizations:
7. Classical Age
- Time Period: circa 800 BCE – 476 CE
- Important Civilizations:
8. Middle Ages
- Time Period: 476 CE – 1453 CE
- Important Civilizations:
9. Early Modern Age
- Time Period: 1453 CE – 1750 CE
- Important Civilizations:
10. Modern Age
Key Points
Three-Age System
The system that divides history into the Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age is known as the Three-Age System.
This system was first formalized in the early 19th century by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen, a Danish archaeologist. He was a curator at the National Museum of Denmark and used the system to organize the museum’s artifacts chronologically.
Thomsen’s classification was based on the types of materials used for tools and weapons, particularly stone, bronze, and iron.
Wider Application
Thomsen’s system was further developed by later archaeologists such as Jens Jacob Asmussen Worsaae, who provided more empirical evidence for the validity of the Three-Age System.
Over time, this framework was expanded by scholars to cover more specific periods, like the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic, and later historical ages like the Classical Age and Middle Ages.
Geographical Variations
While the Three-Age System is widely used in Europe, the time frames and terms vary globally. For example, the development of metallurgy occurred at different times in different regions, so terms like “Bronze Age” or “Iron Age” can have varied significance depending on the location (e.g., Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Europe).
Historical Development
- Christian Thomsen (1788–1865): Invented the Three-Age System.
- Jens Worsaae (1821–1885): Applied and validated the system using fieldwork.
- The system became a foundational tool in archaeology, used to distinguish human technological progress across cultures and regions. It also influenced the study of human prehistory and the development of modern archaeology.
This system remains a common classification for prehistory, especially in Europe and the Near East, but the exact chronology and usage of the ages vary by region.
Examples why the Three-Age System doesn’t work
| Name & Time Period | Civilizations, Buildings, and Mines |
|---|---|
| Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age) Time Period: circa 2.5 million BCE – 10,000 BCE | – Early human groups (Homo erectus, Homo sapiens) – Cave art in Lascaux (France) |
| Neolithic Age (New Stone Age) Time Period: circa 8000 BCE – 3000 BCE | – Early agricultural societies – Çatalhöyük in Anatolia (Turkey) – Göbekli Tepe in Turkey |
| Chalcolithic Age (Copper Age) Time Period: circa 4500 BCE – 3300 BCE | – Varna Culture in Bulgaria – Early Mesopotamian societies (Uruk) |
| Bronze Age Time Period: circa 3300 BCE – 1200 BCE | – Sumerians in Mesopotamia – Ancient Egyptians (Pyramids of Giza) – Minoans in Crete |
| Iron Age Time Period: circa 1200 BCE – 539 BCE | – Assyrians in Mesopotamia – Phoenicians in the Levant – Great Orme Mines in Wales |
| Classical Age Time Period: circa 800 BCE – 476 CE | – Ancient Greeks (Parthenon, Athens) – Romans (Colosseum, Rome) |
| Middle Ages Time Period: 476 CE – 1453 CE | – Byzantine Empire – Islamic Caliphates – Gothic Cathedrals in Europe |
| Early Modern Age Time Period: 1453 CE – 1750 CE | – Ottoman Empire – Ming Dynasty in China – Renaissance Italy (Florence) |
| Modern Age Time Period: 1750 CE – present | – British Empire – Industrial Revolution (factories, railways) – United States (skyscrapers) |