Table of Contents
Names
- Ishtar is the Akkadian name for the goddess
- Inanna is her Sumerian counterpart
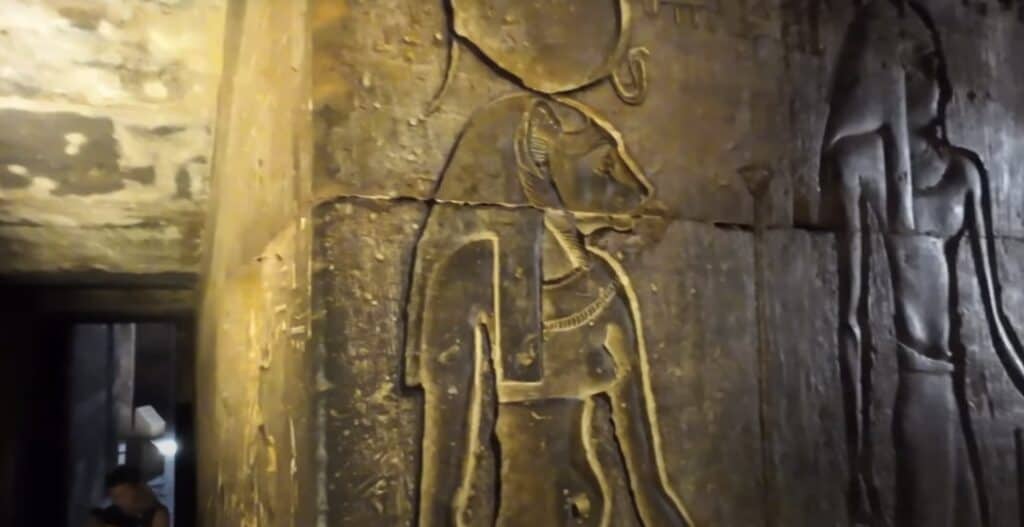
Ishtar is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess associated with love, beauty, war, and fertility. She was one of the most prominent deities in the Mesopotamian pantheon and played a crucial role in the mythology, religion, and culture of the region.
Key Aspects of Ishtar
Attributes and Symbols
Ishtar is often depicted as a powerful and complex figure, embodying contradictory qualities such as love and war.
Her symbols include the lion, representing her fierce and warlike nature, and the eight-pointed star, signifying her association with the planet Venus.
Mythology
One of the most famous myths involving Ishtar is her descent into the Underworld, a journey that represents themes of death and rebirth.
In this story, she descends to the realm of her sister, Ereshkigal, the goddess of the Underworld, to attend a funeral and is trapped there. Her absence causes all fertility on Earth to cease until she is eventually released.
She is also known for her many lovers, including the shepherd Tammuz (Dumuzi), who is associated with the seasonal cycle of death and rebirth.
The goddess Ishtar has withheld the power of fertility, preventing crops from growing and women from bearing children.
Role in Society
Ishtar was worshipped as a goddess of fertility, and her cult often involved rituals intended to ensure fertility and prosperity.
As a goddess of war, she was also invoked in times of conflict, reflecting her dual nature as both nurturing and destructive.
Cultural Influence
Ishtar’s influence extended beyond Mesopotamia, affecting the mythology and religious practices of neighboring cultures.
She has parallels in other ancient cultures, such as the Canaanite goddess Astarte and the Greek goddess Aphrodite.
Ishtar’s multifaceted nature and her significant role in various myths highlight her importance in the ancient Near Eastern world. Her legacy has continued to captivate historians and scholars studying ancient religions and mythologies.