Table of Contents
Great Orme Mines
Located in Wales, UK, these ancient copper mines are estimated to date back to the Bronze Age.
Malachite was extensively mined at the Great Orme Mines in Britain 3,800 years ago, using stone and bone tools. Archaeological evidence indicates that mining activity ended c. 600 BCE, with up to 1,760 tonnes of copper being produced from the mined malachite.
Lake Superior (Michigan,US)
Prehistoric pollution reveals extensive copper mining near Lake Superior.
See: Native Americans Conducted Large-Scale Copper Mining 6,000 Years Ago
Las Médulas
In Spain, Las Médulas is a historic gold-mining site and was one of the largest gold mines of the Roman Empire.
Sutton Hoo
While not a mine, Sutton Hoo in England is famous for the Anglo-Saxon ship burial, which included various precious artifacts like gold and silver, likely sourced from ancient mines.
Laurion
Laurion, located in Greece, was known for its silver mines in ancient times and was a significant source of revenue for Athens during the classical period.
Silk Road Mines
There were various mines along the ancient Silk Road, spanning from China to the Mediterranean, where different minerals including gold, silver, and gemstones were mined.
King Solomon’s Mines
This is a biblical and historical term referring to mines supposedly owned or worked by King Solomon in the ancient world. The exact location, however, remains a mystery and a topic of much speculation.
Rosia Montana
In Romania, these are ancient gold mines that were extensively exploited by the Romans.
Swaziland Iron Ore Mine
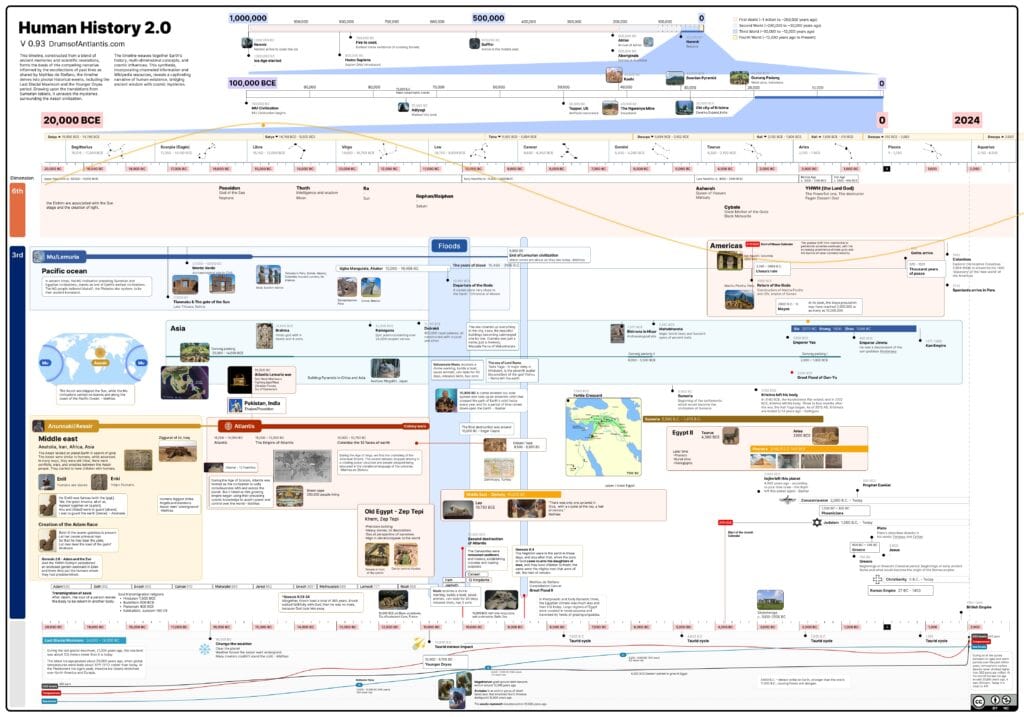
The Ngwenya Mine, located in the Hhohho Region of Swaziland, is one of the world’s oldest known mines. It’s an iron ore mine situated amidst the rugged mountains of western Swaziland, near the border with South Africa.
- The Ngwenya Mine is estimated to be around 43,000 years old, making it one of the oldest mines known to humans.
- Archaeological evidence suggests that the ancient people of the region mined hematite, an iron ore, from this site.
- The ancient miners likely used primitive tools made of bone, wood, and stone to extract the iron ore from the earth.
- These early humans would have heated the hematite to extract the iron, possibly for creating tools, weapons, or decorative items.
- The Ngwenya Mine holds significant cultural importance for the Swazi people and is considered a national heritage site.
- Archaeological excavations have revealed various artifacts, including mining tools and pottery shards, providing valuable insights into the lives of ancient miners.
- Due to its historical and archaeological significance, efforts have been made to preserve the Ngwenya Mine site.
- Conservation initiatives aim to protect the ancient mining pits and artifacts while allowing researchers to study the site.
Malachite
Malachite was mined from deposits near the Isthmus of Suez and the Sinai as early as 4000 BCE.
Archaeological evidence indicates that the mineral has been mined and smelted to obtain copper at Timna Valley in Israel for more than 3,000 years. Since then, malachite has been used as both an ornamental stone and as a gemstone.